Introduction to Ansys Twin Builder for Mechanical Systems
Introduction to Ansys Twin Builder for Mechanical Systems
one-day courseAnsys Twin Builder enables engineers to accurately and quickly design complex mechanical, power electronics and electrically controlled systems. In industries such as automotive, aerospace and industrial automation, organizations use Twin Builder to identify problems in the early design stages that other simulation or build-and-test methods cannot detect.
This course provides an introduction to Ansys Twin Builder for Mechanical Engineers. The course focuses on hands on workshops, and students solve problems ranging from spring-mass-damper dynamic systems to hydraulic systems including transient effects. Workshops also include modeling of a Pong game using co-simulation with the Ansys Mechanical Rigid Body Dynamics tool as well as use of Ansys Mechanical and Ansys CFD Reduced Order Models in fluid systems.
Workshop 1 - Spring-Mass-Damper Mechanical Systems
Workshop 1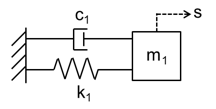
Transient response of ideal single degree of freedom mechanical system (simple mass spring damper)
Workshop 2 - Hydraulic Systems including Transient Effects
Workshop 2 
Transient and frequency response of ideal two degree of freedom mechanical system (simple multi-mass-spring-damper)
Workshop 3 - Co-Simulation using Ansys Mechanical Rigid Body Dynamics
Workshop 3a 
Transient simulation of a hydraulic system comprised of ideal linear pipes and ideal pump
Workshop 3b 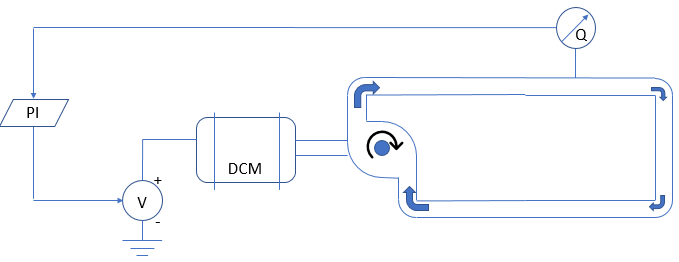
Transient simulation of a hydraulic system comprised of non-linear pipe and a realistic pump with feedback control
Workshop 4 - Hydraulic Systems with Ansys Mechanical Reduced Order Models
Workshop 4 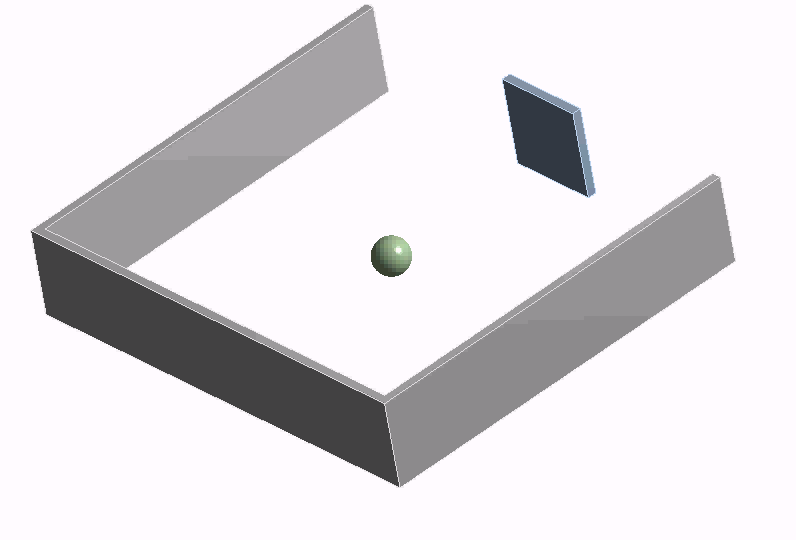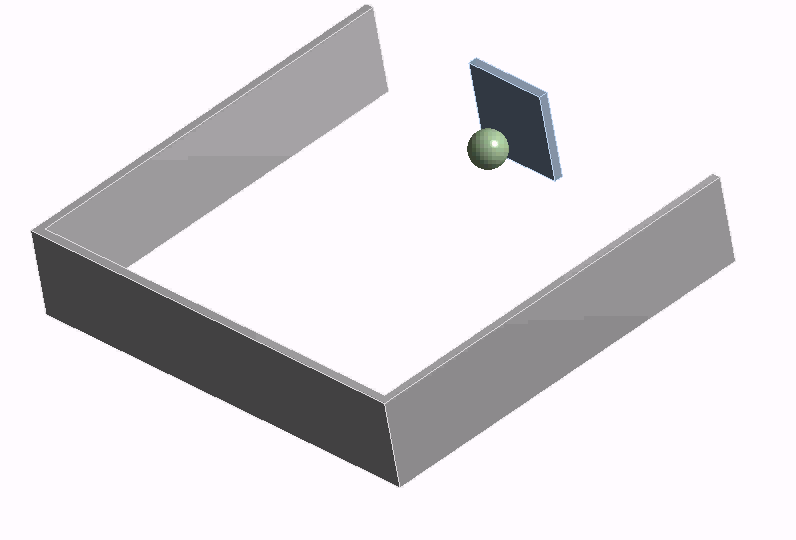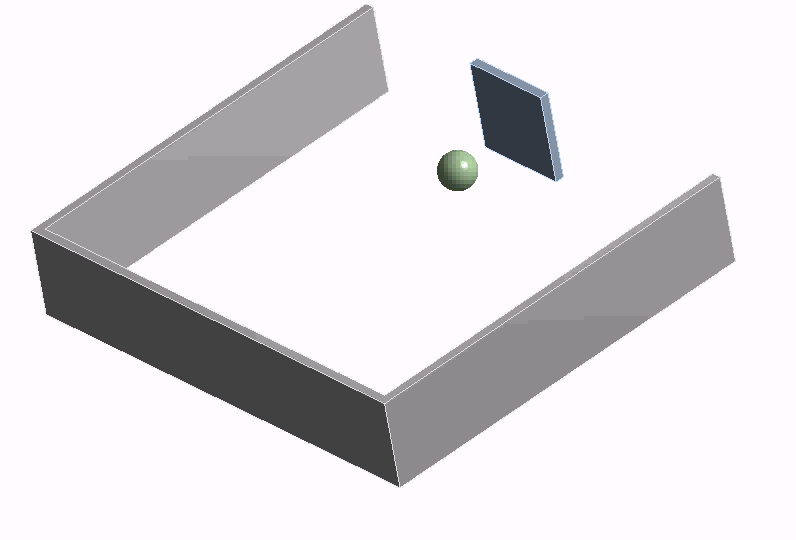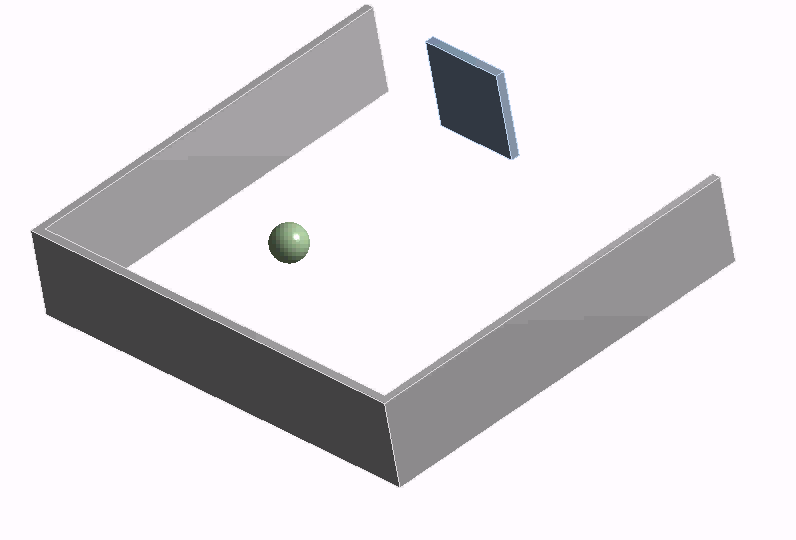
Transient simulation of ping-pong game with feedback control in Twin Builder using co-simulation with Rigid Body Dynamics (RBD)
Workshop 5 - Fluid Systems with Ansys CFD Reduced Order Models
Workshop 5
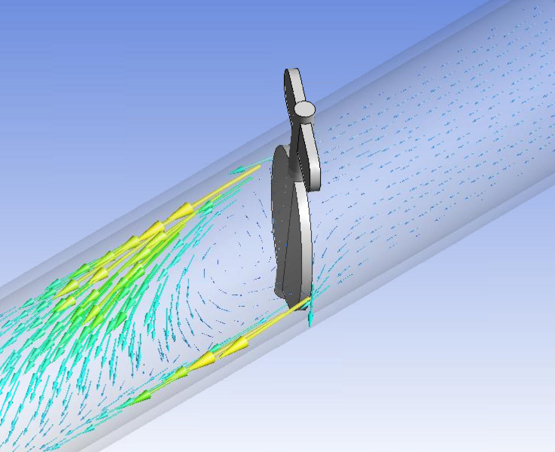
Transient simulation of gas regulator response in Twin Builder using Ansys Mechanical Reduced Order Model (ROM) to represent non-linear diaphragm structure.
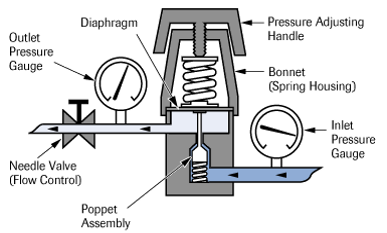

Workshop 6
Workshop 6
Transient simulation of piping system with position controlled butterfly valve where valve flow characteristics originate from an Ansys Fluent Reduced Order Model (ROM).